Nanostructured composites from latex nanoparticles
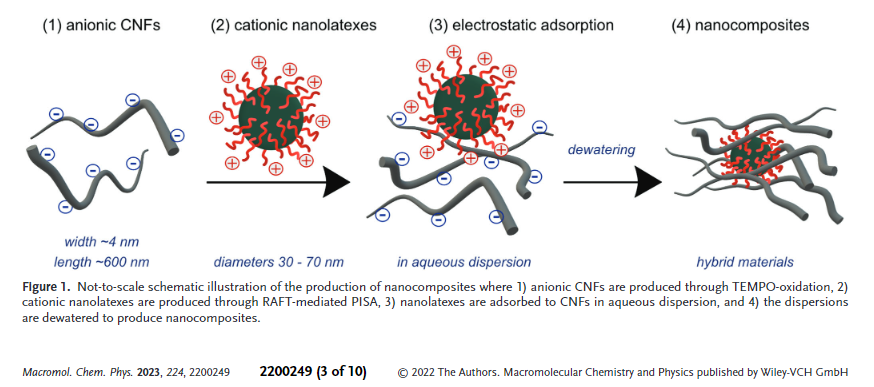
Latex nanoparticles with controllable physico-chemical properties, such as size, rigidity and surface functionality, have shown great promise in modifying and tailoring macroscopic properties of cellulosic nanomaterials. For instance, it has been found that cationic nanoparticles can stiffen or plasticize cellulose nanopapers depending on additive amount. The impact of nanoparticle shell functionality will be further investigated […]
Soft highly swelling fibres by alkali-activated chemical modification
To make cellulose fibres more flexible and malleable, components inside the fibre must be properly modified, that is, the lignin, hemicellulose or cellulose needs to be at least partly transformed into a proper derivative. Several cellulose derivatives are today produced through chemical reactions that involves formation of ether bonds. To reach sufficient efficiency, these reactions […]

