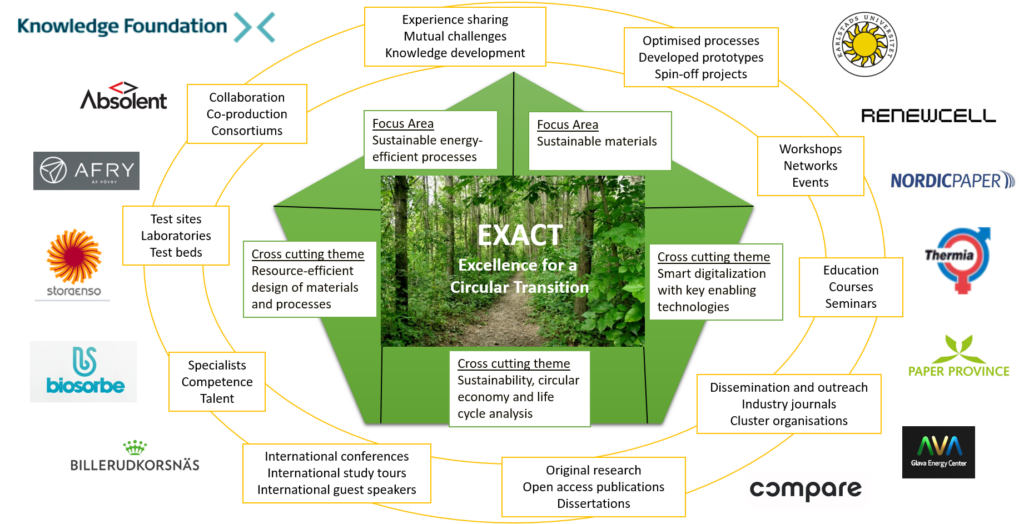
EXACT – Excellence in Advancing for a Circular Transition
The research school ‘EXACT- Excellence in Advancing for a Circular Transition’ combines bioeconomy with smart digitalization, in a collaboration between the two research groups Pro2BE and DAMI4.0 at Karlstad University. The Ph.D. students will develop energy-efficient digitalized production processes or products and high-quality bio-based materials. The aim of this research school is to contribute to […]
EXACT – Excellence in Advancing for a Circular Transition Läs mer »